Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Air-Conditioning and Refrigeration Corporation (MHI-AC&R), a Group company of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (MHI), has newly developed a large-capacity brine refrigeration system adopting a nitrogen (N2) refrigerant having both zero ozone depletion potential (ODP)(1) and zero global warming potential (GWP)(2). The new system can accommodate even cryotemperature needs, placing it at the pinnacle of industry offerings(3). The Company has just delivered a unit of the new system to The Honjo Chemical Corporation (Neyagawa, Osaka), a manufacturer of organic chemicals and other products, and further sales in the domestic market will be pursued going forward.
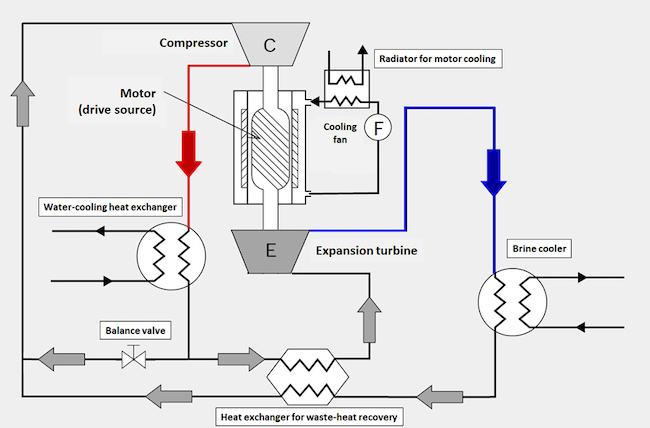 |
| Large-capacity air-refrigerant (N2) brine refrigeration system flowchart |
The new system can refrigerate at ultra-low and cryo-temperatures (brine temperature: -45℃ to -100℃) through application of MHI-AC&R’s proprietary (patented) air refrigeration cycle technology. The unit also features one of the industry’s most compact sizes, enabling easy handling and transport. Its compression expansion machine incorporates MHI Group’s accumulated high technologies in gas turbines. In addition to capturing the energy generated during air expansion cooling and using it as drive power, stable operation is achieved through the integration of high technologies such as energy-saving inverter control.
The new refrigeration system contributes significantly to curbing global warming through the adoption of N2, a natural refrigerant having zero environmental impact. In recent years, initiatives to prevent climate change have accelerated in momentum. In Japan, since April 2015, when the Act on Rational Use and Appropriate Management of Fluorocarbons(4) went into effect, the low-temperature refrigeration machine market has been called on to adopt low-GWP refrigerants. Internationally, in tandem with implementation of the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer in January 2019, along with revisions to the Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer, production of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) substitutes and phased reduction in energy consumption have become mandatory.
Today, because there are few refrigerant options in the ultra-low-temperature refrigeration field, many refrigeration systems continue to use CFC refrigerants. However, demand for CFC-free refrigeration systems is steadily rising in order to mitigate impact on the environment. The refrigerant used in MHI-AC&R’s new refrigeration system uses nitrogen, which accounts for approximately 78% of air content, so it is safe both to the environment and to humans. Use of a CFC-free refrigerant also eliminates the inspection procedures mandated under the Act on Rational Use and Appropriate Management of Fluorocarbons, and the new refrigerant is also exempt from the High Pressure Gas Safety Act which regulates the production of high-pressure gases and their consumption, etc. Another benefit is the adoption of magnetic bearings in the system’s compression expansion machine, which eliminates the need for lubricating oil and enables a virtually unlimited service life, thereby helping to ease the user’s maintenance and operating burdens.
(1) ODP is a coefficient expressing a refrigerant’s ozone depletion potential compared to the previously widely used CFC-11 (trichlorofluoromethane), which is assigned a value of 1.0. The lower the ODP value, the smaller is the deleterious impact on the ozone layer.
(2) GWP is a coefficient expressing a refrigerant’s global warming potential compared to CO2, which is assigned a value of 1.0. The lower the GWP, the higher is the refrigerant’s environmental performance.
(3) Based on MHI-AC&R’s in-house survey.
(4) The Act on Rational Use and Proper Management of Fluorocarbons is a totally revised update, carried out in April 2015, to the original Fluorocarbons Recovery and Destruction Law enacted in 2001. Under the revised legislation, commercial refrigeration condensing units and stationary refrigeration units with a refrigeration capacity exceeding 1.5 kilowatt (kW) (approx. 2HP) are required by 2025 to adopt refrigerants with a GWP below 1500 (CO2 =1).
Delivery Overview
Client and destination: The Honjo Chemical Corporation, Naoshima Organic Chemical Plant
(Naoshima-cho, Kagawa-gun, Kagawa Pref.)
Intended usage: Removal of heat of reaction produced during production of organic chemicals
Specification: Brine temperature -80degC (down to -100degC)
About MHI Group
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) Group is one of the world’s leading industrial groups, spanning energy, logistics & infrastructure, industrial machinery, aerospace and defense. MHI Group combines cutting-edge technology with deep experience to deliver innovative, integrated solutions that help to realize a carbon neutral world, improve the quality of life and ensure a safer world. For more information, please visit www.mhi.com or follow our insights and stories on spectra.mhi.com.
Topic: Press release summary



